Articles
Blood physiology and overview
The webpage on Blood Physiology from Physiopedia covers various components and functions of blood. It explains blood plasma (including its role in transporting gases, nutrients, and waste), erythrocytes (red blood cells), and leucocytes (white blood cells), detailing their structure, function, and production. Additionally, it discusses hematopoiesis, blood disorders, and how blood plays a crucial role in immune defense, acid-base balance, and temperature regulation. You can explore the full article:
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Blood_Physiology
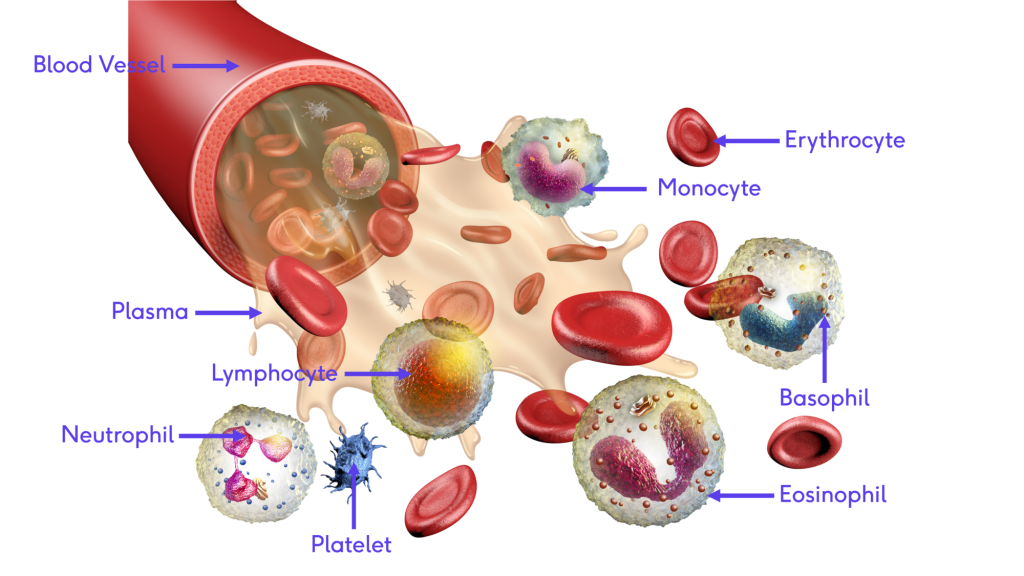
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
The Cleveland Clinic article explains the vital role of red blood cells (RBCs) in transporting oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carrying carbon dioxide back for exhalation. RBCs are produced in the bone marrow and contain hemoglobin, which binds to oxygen. Disorders affecting RBC count, such as anemia or polycythemia, can lead to health issues. Maintaining healthy RBCs involves a diet rich in iron, B vitamins, and avoiding smoking. For more details, visit the full page:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21691-function-of-red-blood-cells
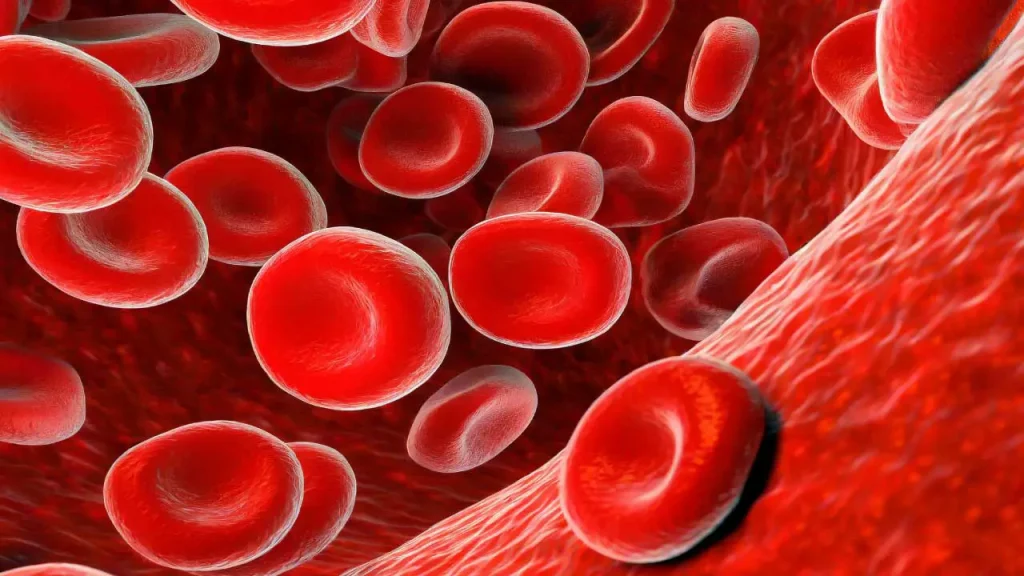
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
The Cleveland Clinic article explains the role of white blood cells (WBCs) in the immune system, defending the body against infections by identifying and destroying harmful organisms. It describes the five types of WBCs, their formation in the bone marrow, and their function in immune response. The article also covers conditions like low or high WBC counts and how they are measured. To learn more, visit the full page:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21871-white-blood-cells
Thrombocytes (Platelets)
The Cleveland Clinic article explains the role of platelets in blood clotting. Platelets are cell fragments that form plugs to stop bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. They are produced in the bone marrow and stored in the spleen. Disorders like thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) or thrombocytosis (high platelet count) can affect clotting. The article also discusses how platelets function in the coagulation process and common conditions affecting them. For more details, visit the full page:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22879-platelets
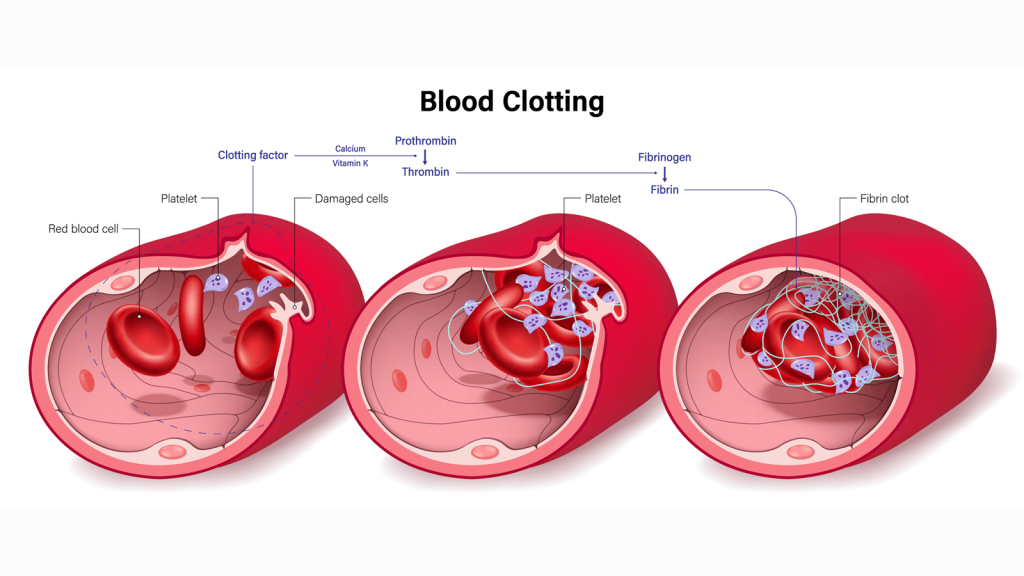
Process of Platelet Clotting
The MSD Manual explains the process of blood clotting, also known as hemostasis. It involves three key steps: blood vessel constriction, platelet activation and aggregation, and the activation of clotting factors that form fibrin, which solidifies the clot. The article also highlights the importance of controlling clot formation to prevent excessive bleeding or clotting, which can lead to conditions like stroke or heart attack. Medications like aspirin, anticoagulants, and thrombolytics can influence clotting, either preventing or dissolving clots. For more details, visit the full page:
https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/blood-disorders/blood-clotting-process/how-blood-clots
Videos
Blood is a complex tissue composed of plasma, red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. Plasma is the liquid component, transporting nutrients, hormones, and waste products. RBCs, containing hemoglobin, carry oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide. WBCs are involved in immune responses, defending against pathogens. Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding. Blood circulates through blood vessels, maintaining homeostasis, regulating body temperature, and supporting organ function. Check out the videos for detailed information.
Part 1
Part 2
